The Significance of Studying Soil Moisture Transformation in Arid Regions
China's vast land and resources have also created weather conditions in different regions. In the north and west of China, water shortage drought is an important factor affecting residents' lives, agricultural growth, and economic development. Especially in agricultural production, in various arid and semi-arid areas, due to lack of soil moisture, it is necessary to use water scientifically and reasonably, measure soil moisture content in time with a soil moisture meter, and study various movements of soil moisture, Conversion, evaporation, absorption, etc., have important implications for the rational use of soil moisture in arid regions.
The dynamics of soil moisture are affected by the effects of water supplementation (rainfall, groundwater regulation, etc.) and water consumption (surface evaporation, vegetation transpiration, etc.). Through the secondary distribution of light, heat, water and other resources, the terrain has direct and indirect effects on the ecological processes of water supply and water consumption, resulting in spatial and temporal differences in soil moisture content and grassland productivity under different topographic conditions. There are different correlations between vegetation productivity and soil moisture at different temporal and spatial scales of biological systems.
Therefore, it is of great significance to carry out multi-scale research to elucidate various ecological processes that affect soil moisture migration and grassland productivity spatial-temporal differentiation. Based on the observation of soil moisture and grassland biomass in desert grassland of Inner Mongolia, this paper discusses the influence of topography on the spatial and temporal heterogeneity of soil moisture and biomass, and analyzes the relationship between soil moisture content at different depths and grassland biomass in different growth seasons. The spatial-temporal distribution of soil moisture and biomass under different topographic conditions and the key ecological factors affecting water migration and plant growth are revealed, providing a theoretical basis for explaining the stability of desert ecosystems and in-depth study of desertification areas.
The low noise issues of lasers are due to the competition of mode in Laser resonant cavity, which lead to high frequency jitter of output power. Through special design for laser resonant cavity and other components, the laser amplitude noise can be reduce efficiently. CNI low noise laser can be widely applied to DNA sequency, cell sorting, spectrum analysis, interference measurement, laser holography, photo processing and biomedical and other fields.
CNI offers low noise lasers in wavelengths from ultraviolet to infrared (360~1550 nm).
Features:
Beam spot pattern: TEM00
M²: <1.1
Pointing stability: <5μrad/℃
Constant temperature (23±3℃) noise: -52dB
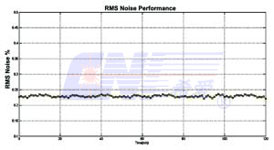
Noise stability (RMS@4h): <0.2%
Bandwidth: 20Hz~20MHz
Examples of the testing results
 |
 |
 |
|
Testing chart of noise stability (RMS@2h 20Hz~20MHz) |
Testing chart of noise stability in variable temperature (10~35℃) |
Testing chart of noise stability in constant temperature (23±3℃) |
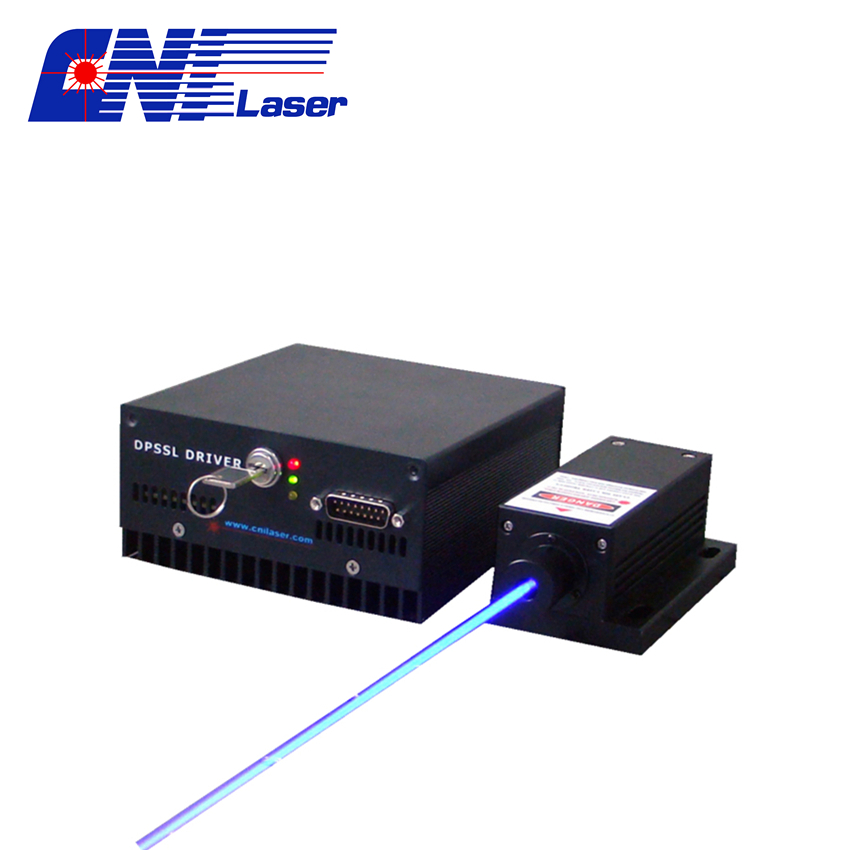
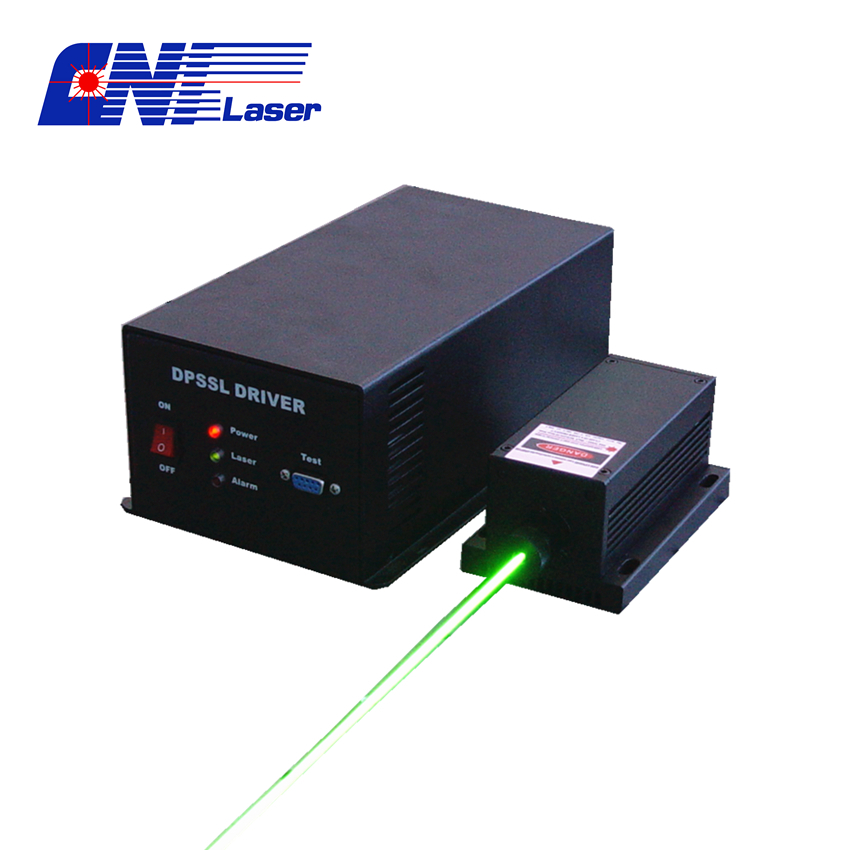


Low Noise Laser,Noise in Laser Diodes,Solid Laser Beam,Wavelength of Red Laser
Changchun New Industries Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.lasersciences.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)